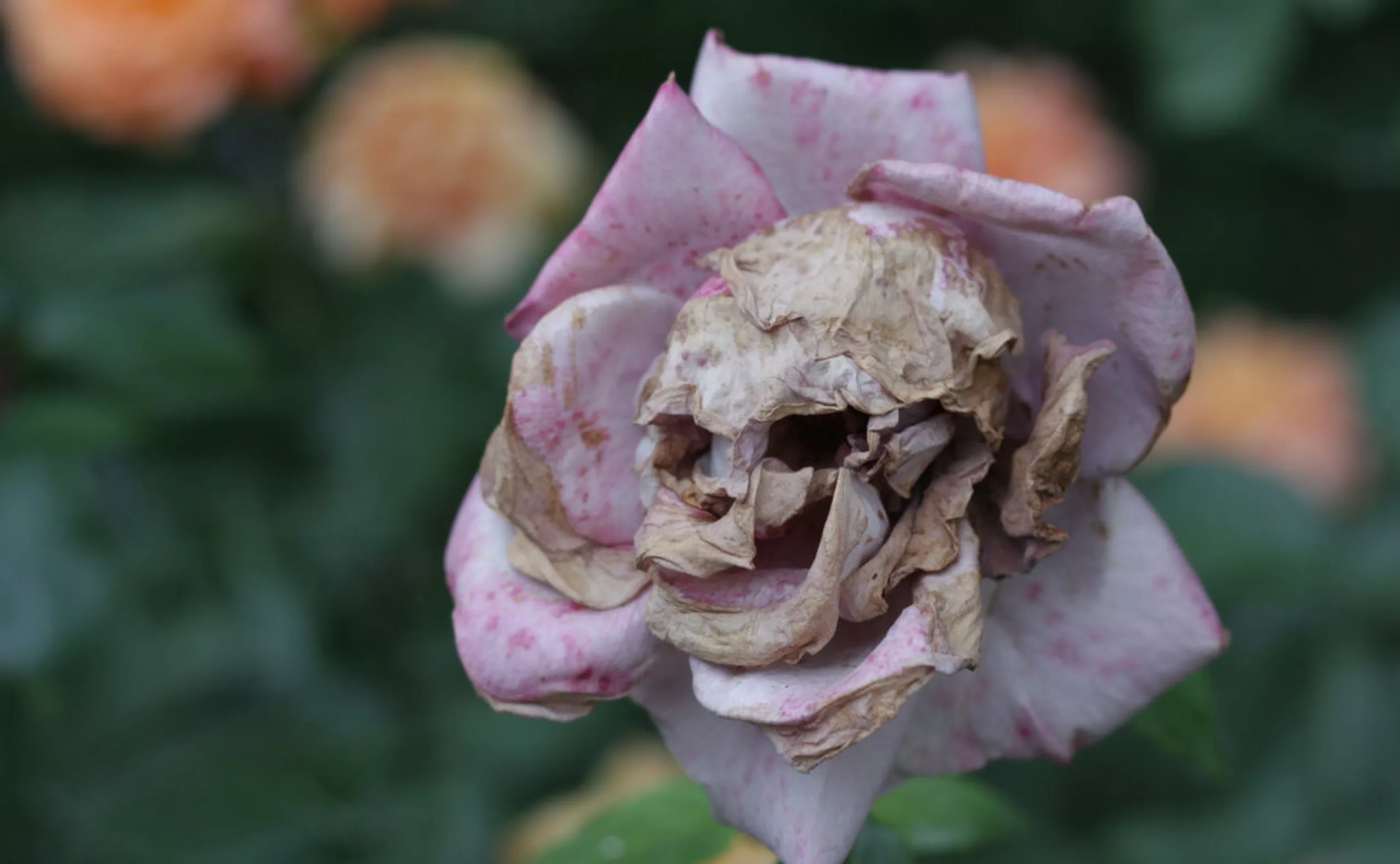
Pareidolia, or the art of seeing faces everywhere !

A few days ago, we told you how to make your face disappear in public using the mask of a certain Leo Selvaggio.
Today, we are going to tell you how, and above all why, you can see faces where there are none !
What is pareidolia ?
A pareidolia is a kind of optical illusion that consists in associating a shapeless, ambiguous visual stimulus with a clear, identifiable element, often a human or animal form. It’s this astonishing ability of the human brain to “make sense” of things where there really is none, the cognitive mechanisms of which are still poorly understood.
More generally, pariedolia allows us to grasp that all perception is construction: it is the subject who gives meaning to perceptual stimuli. Examples of this in everyday life are legion: familiar shapes in clouds and in various stains and objects. In fact, people sometimes observe shapes in their environment that seem meaningful to them. This phenomenon is common in photographs.
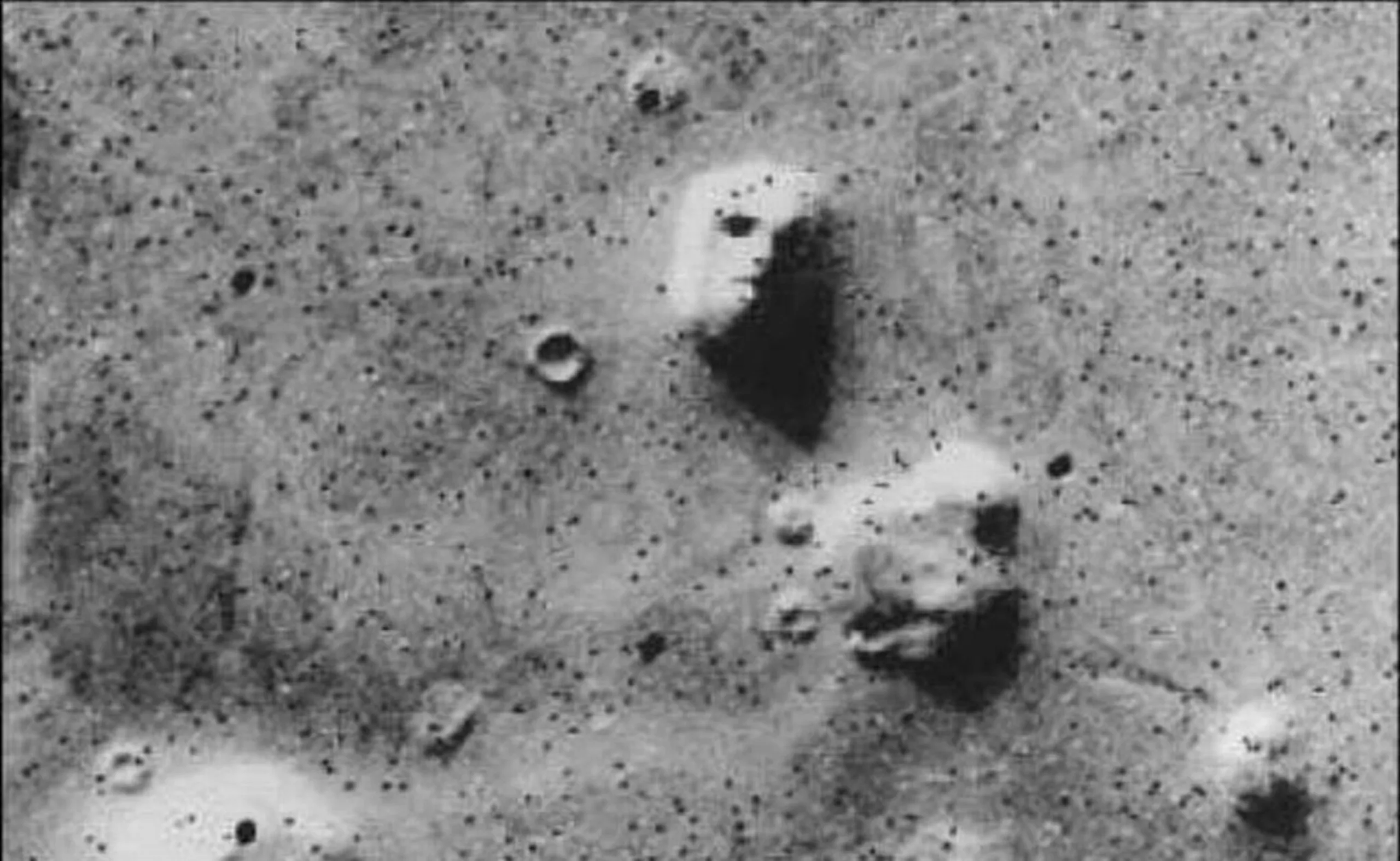
The most famous example is probably the “Face of Mars“, an optical illusion due to the particular succession of light and shadow zones. Pareidolia is also used clinically in the famous Rorschach test. The subject gives meaning to inkblots presented to him or her according to his or her own mental representations, thus providing an insight into some of his or her psychic dynamics.
The phenomenon of pareidolia can be very disturbing for some people, who may consider it a sign of a deceased person, for example. Whatever the final explanation for this phenomenon, it is often important to try and grasp its meaning for the individual, beyond its strange nature.
An instict for survival
Although it can appear as the result of a brain dysfunction, pareidolia is generally caused by the natural tendency to assimilate new perceptions with those already known and catalogued. This is mostly useful for identifying a new object as belonging to a known category, but can lead to errors. The stroop effect is another variety of this same preference of the senses to interpret a perception by comparing it with those already known. To put this effect to the test, simply name the color in which each of these words is written as quickly as possible:
Test 1 : Red – Blue – Orange – Green – Purple – Pink
Test 2 : Pink – Green – Red – Purple – Orange – Blue
If you’re as “untalented” as I am, it will easily take you 2 seconds longer to read the second line !
In short, this ability may derive from an evolutionary advantage that has led to a hypersensitivity to detecting presence, which favors survival but not necessarily accuracy. So, for example, errors are almost all in the same “direction”: false positives (recognizing a presence that isn’t there) rather than false negatives (not recognizing a presence).
Unlike other optical illusions, which are based on the universal laws of human perception, in the case of pareidolia, everyone can see something different. In particular, humans tend to guess faces as soon as an object resembles one. Expectations, predispositions and culture all have an impact on these “projections”. The Rorschach test, for example, is based on this cognitive function. Pareidolia is therefore a complex cognitive phenomenon.
[Source Wikipédia]
Leonardo da Vinci also wrote about pareidolia as an artistic and poetic tool.
“If you look at all the walls mottled with various stains or with a mixture of different types of stones , if you are about to invent a scene you will be able to see a resemblance to various different landscapes adorned with mountains, rivers, rocks , trees , plains, wide valleys and various groups of hills“, he writes in his notes.
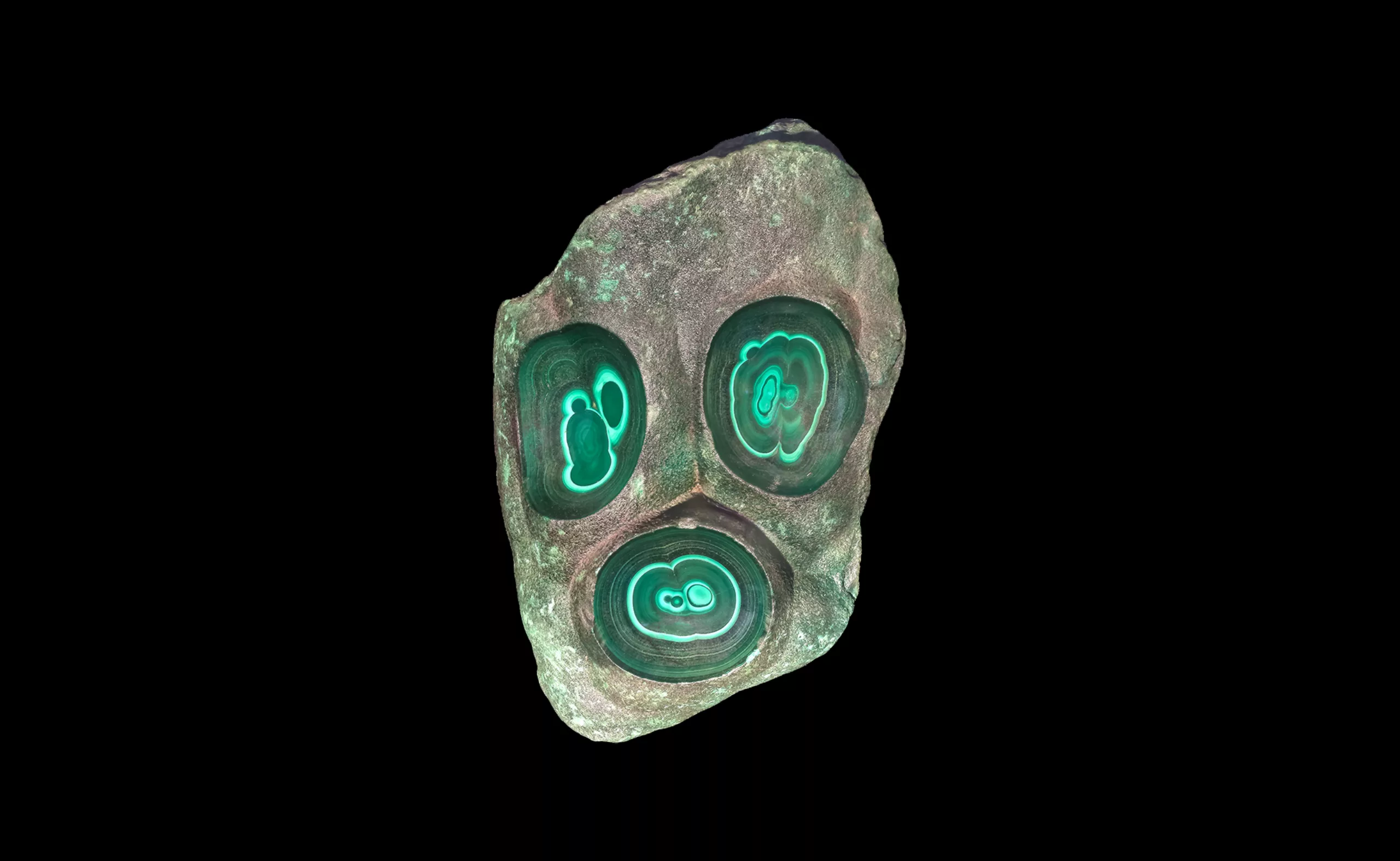
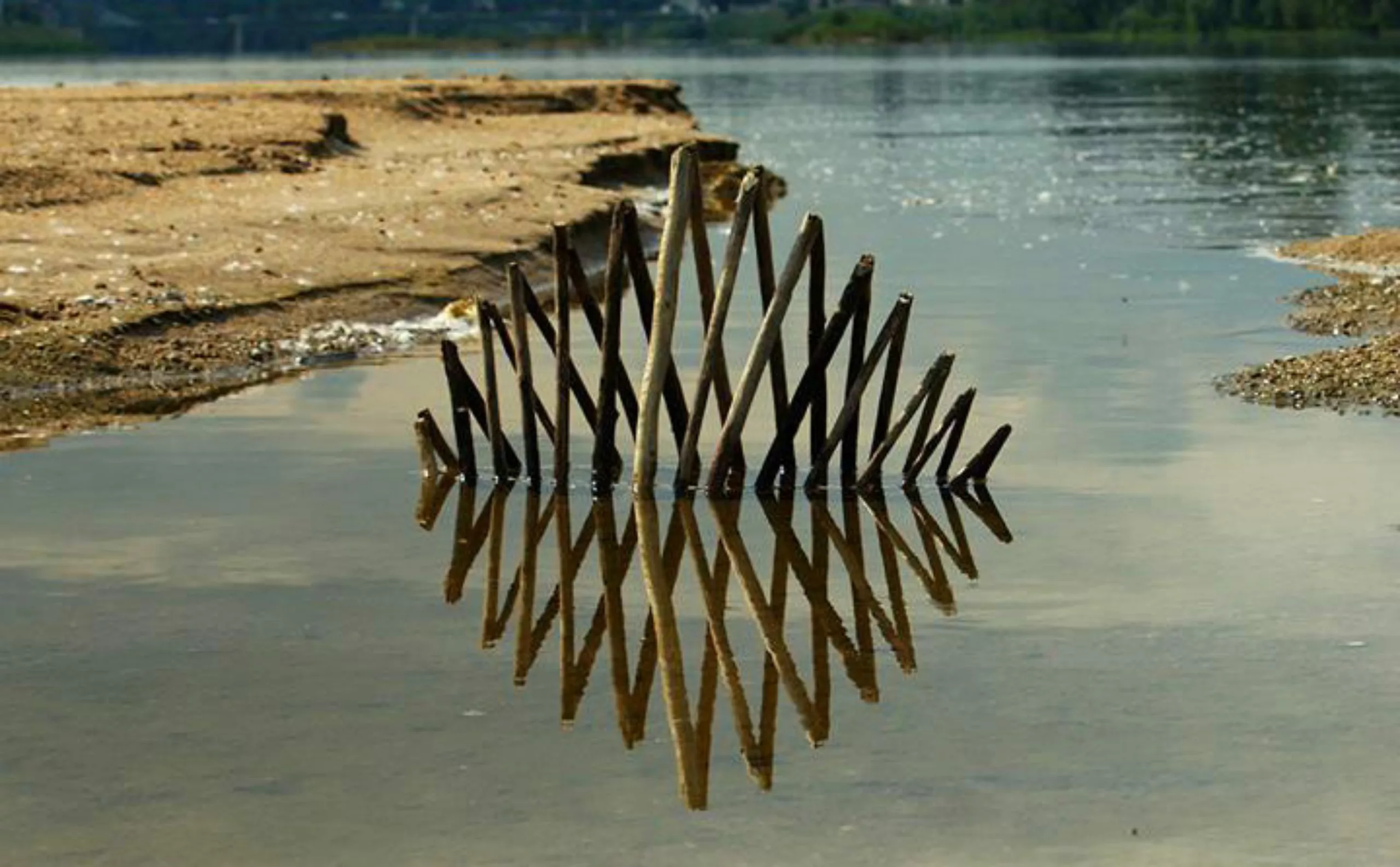
Some examples in pictures…

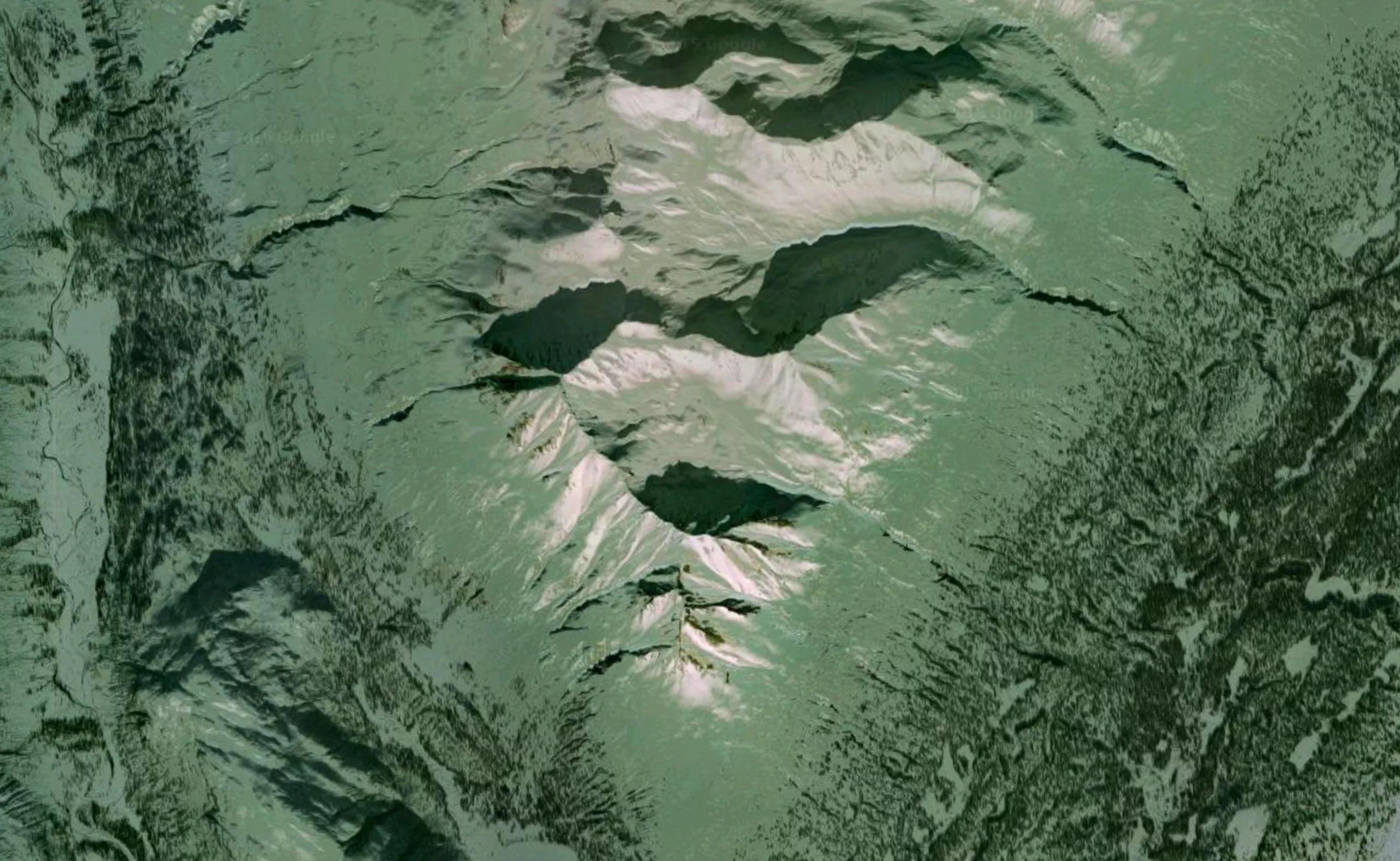
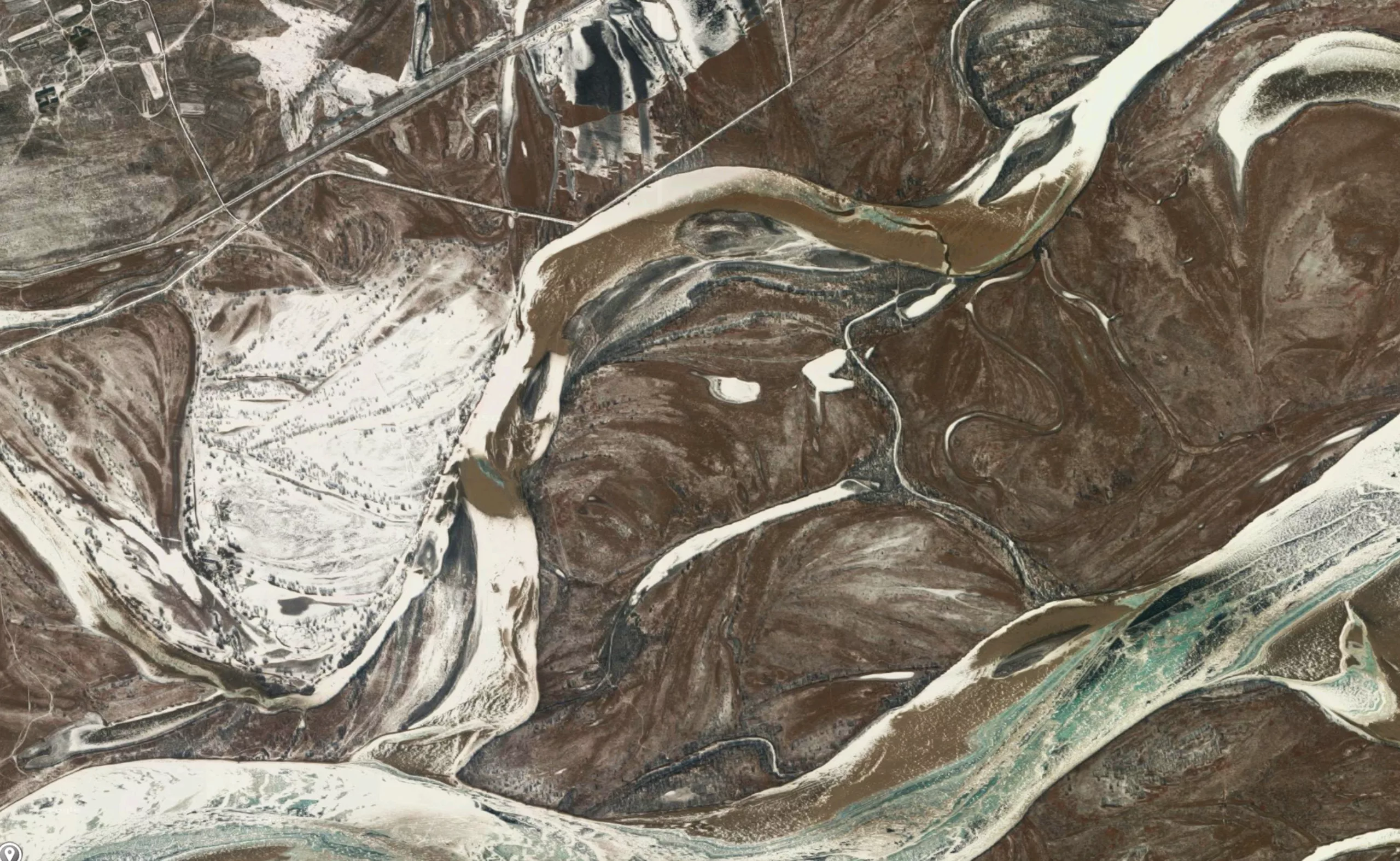
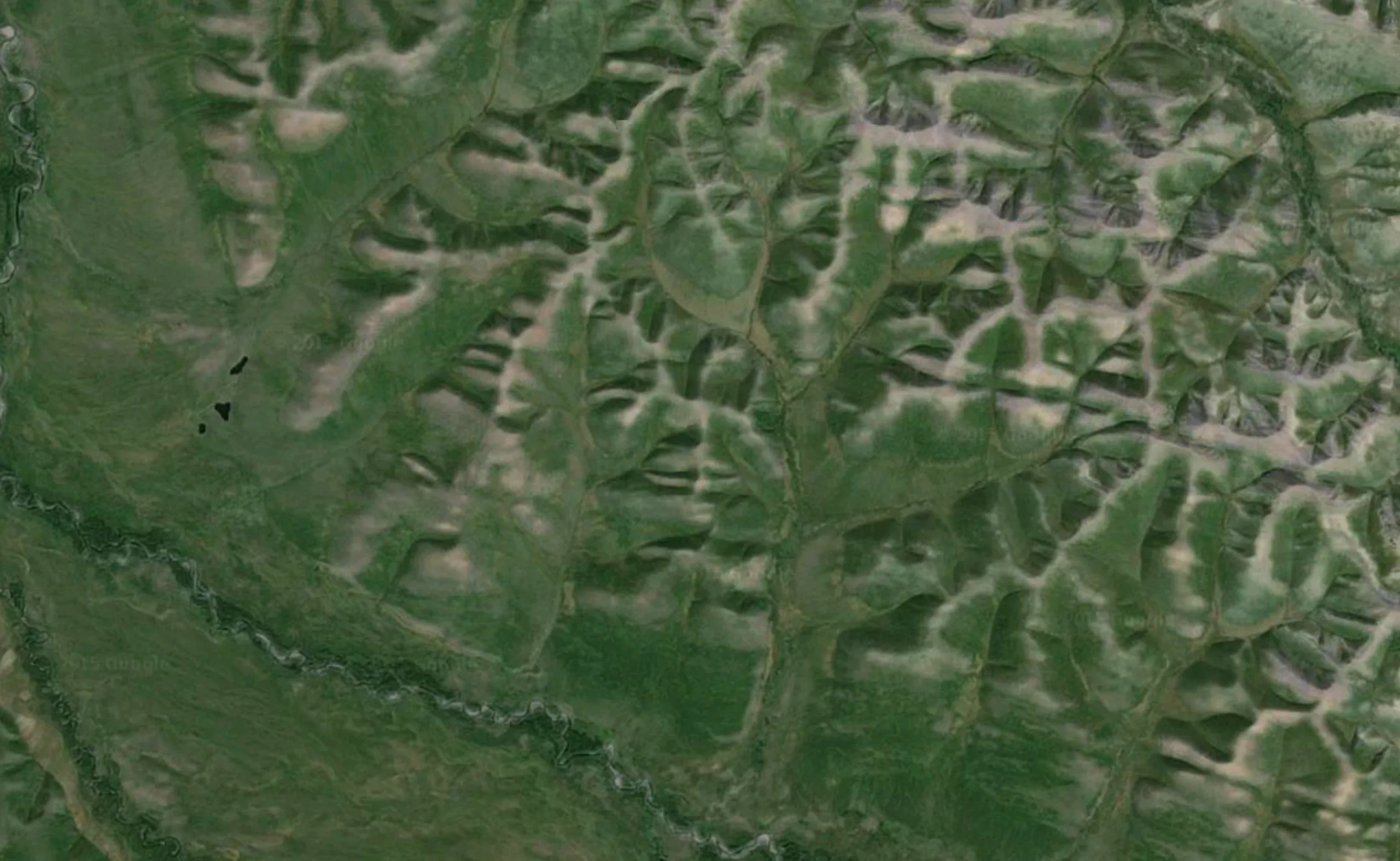
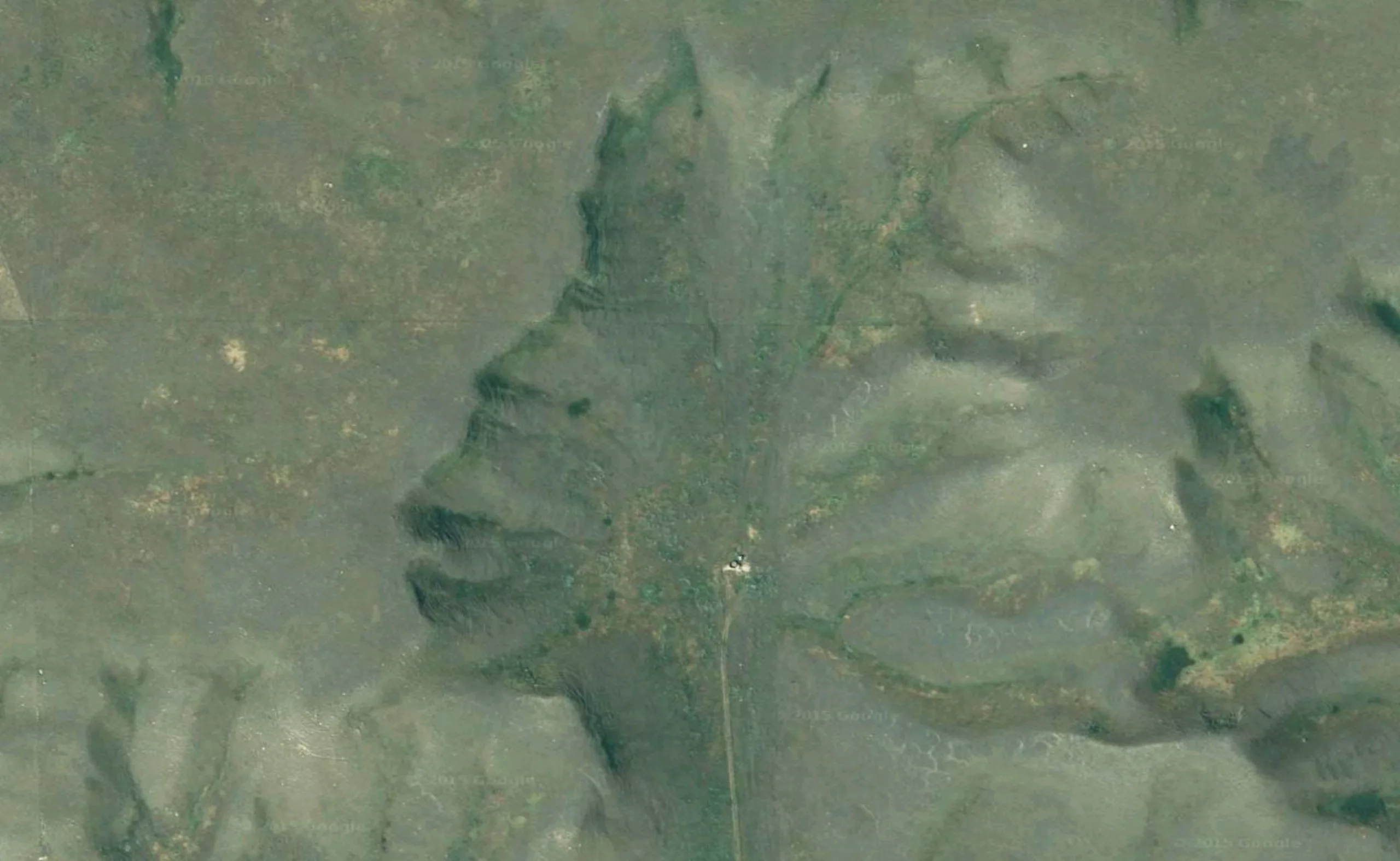
Faces from the sky
In the same spirit, the Berlin studio Onformative has designed a program to locate faces seen from the sky in Google Earth.
This “robot”, specialized in pareidolia, flies from one side of the earth to the other, using the different zoom levels available, in search of hidden faces.
Below is a short demonstration video and some of the “faces” detected.
Pareidolia in painting.
Of course, the most illustrious representative of the pareidolia category in painting is the Italian master Giuseppe Arcimboldo !
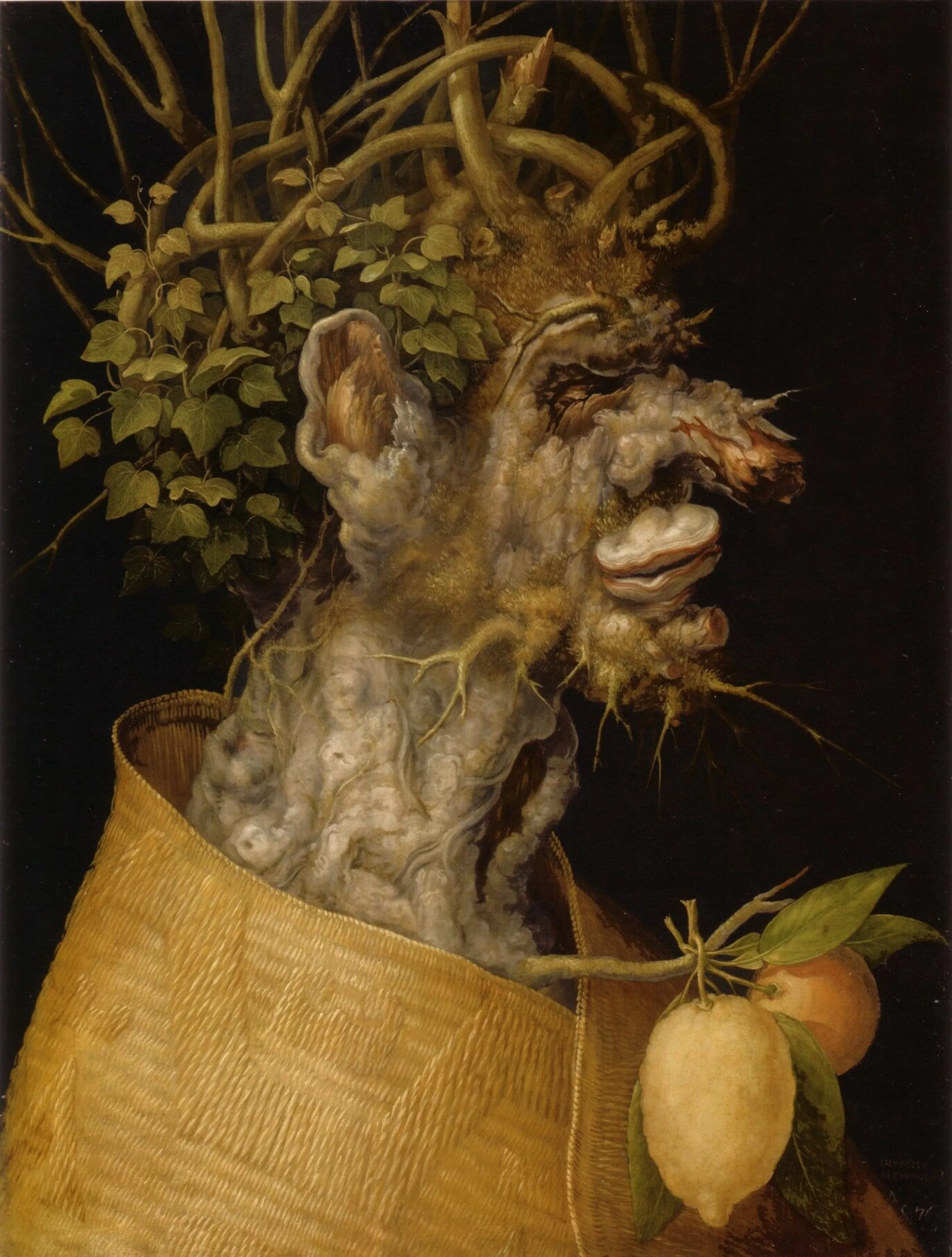
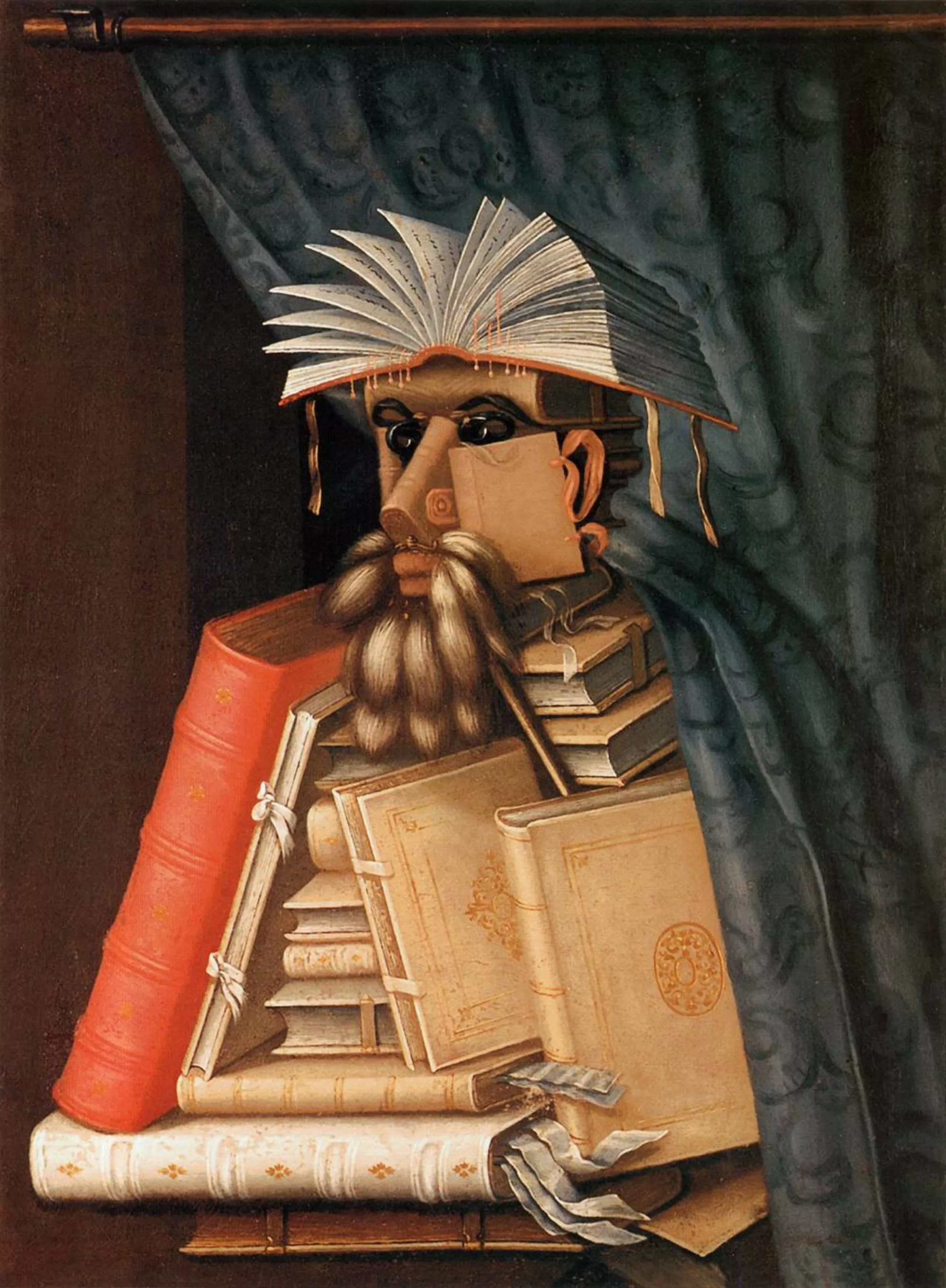
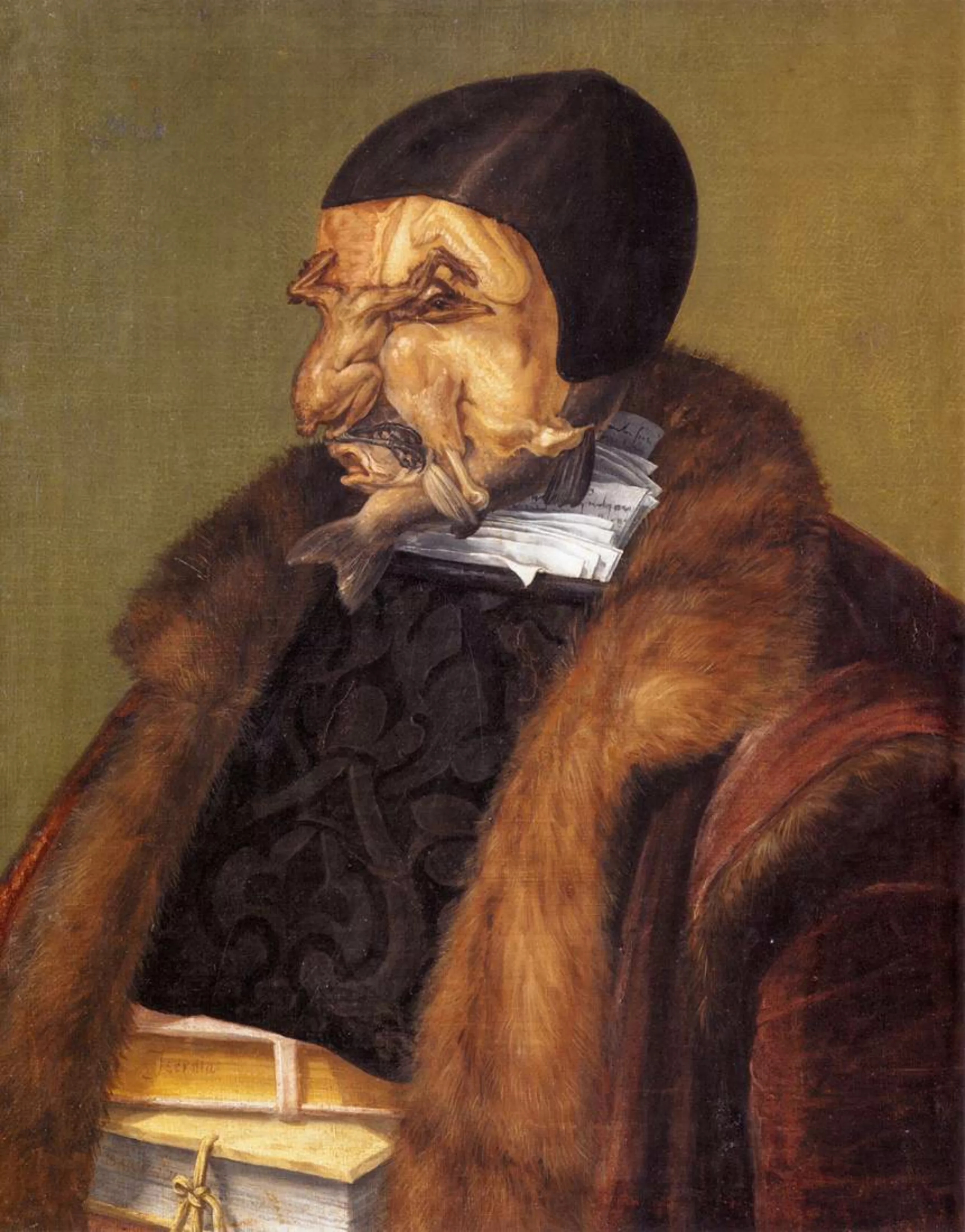



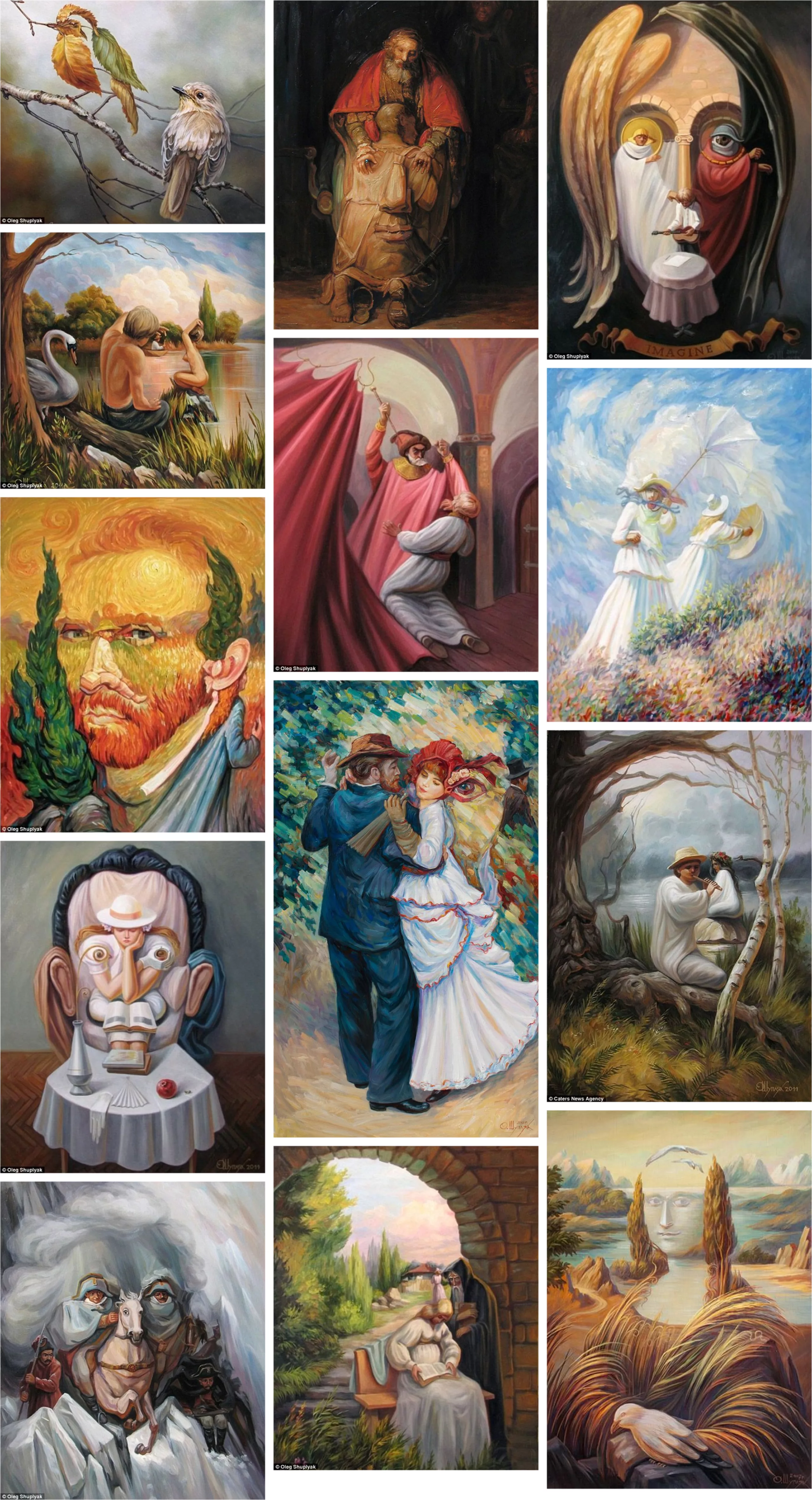
Ukrainian surrealist painter Oleg Shuplyak has fun hiding faces in his bucolic, kitschy landscapes.
Here, faces and landscape become one. René Magritte was also known to be a fan of this kind of game, but now he has found a disciple. It will be up to you to find John Lennon, William Shakespeare, Vincent Van Gogh, Leonardo da Vinci…







